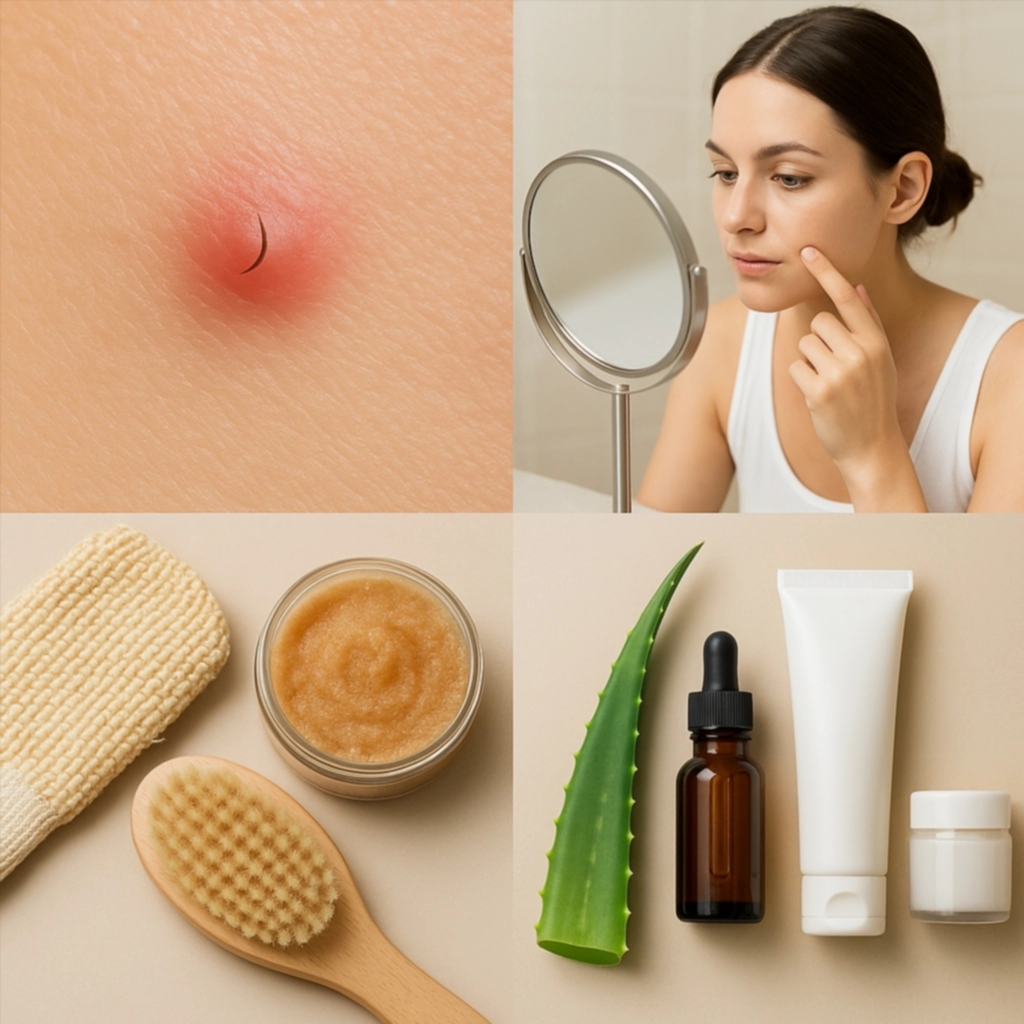
Ingrown hairs, or ingrown hair in English, are a common dermatological issue that can affect people of any age, gender, or skin type. They often appear after hair removal procedures such as shaving, waxing, or tweezing, and though usually benign, they can cause discomfort, inflammation, and aesthetic concerns. In this article, we will explore the nature of ingrown hairs, their causes, how to prevent them, and the most effective treatments from both home remedies to medical approaches.
Содержание
- 1 What is an Ingrown Hair?
- 2 The Science Behind the Problem
- 3 Common Causes of Ingrown Hair
- 4 Symptoms and Identification
- 5 Areas Most Commonly Affected
- 6 Potential Complications
- 7 Prevention of Ingrown Hair
- 8 Treatment Options
- 9 Home Remedies with Natural Ingredients
- 10 When to See a Doctor
- 11 Cultural and Linguistic Note: «Ingrown Hair» in English
- 12 Conclusion
What is an Ingrown Hair?
The term ingrown hair refers to a condition where a hair grows back into the skin instead of rising up from it. Instead of following its natural path outward, the hair curls or gets trapped under the surface of the skin, leading to a small bump, often resembling a pimple. These bumps can be red, inflamed, itchy, and sometimes painful. In more severe cases, they may even become infected.
Ingrown hairs are especially common in areas where the skin is frequently shaved or waxed — such as the face, neck, legs, armpits, and the bikini line.
The Science Behind the Problem
To understand the issue, we need to look at the anatomy of hair growth. Each hair grows from a follicle that lies under the skin. When the hair emerges, it should grow straight out of the follicle. However, if the hair is cut too short or removed by the root (as with waxing), the new hair might struggle to break through the surface. In people with curly or coarse hair, this tendency is heightened, as the hair naturally bends back toward the skin.
When the sharp tip of the hair re-enters the skin, the body identifies it as a foreign object and triggers an inflammatory response, which can lead to redness, swelling, and pus.
Common Causes of Ingrown Hair
- Improper Shaving Techniques
Shaving too closely, especially with multiple-blade razors, can cause the hair to be cut at an angle, increasing the risk of re-entry into the skin. - Tight Clothing
Friction from tight clothes, particularly in areas like the thighs, groin, or underarms, can cause hair to bend and grow sideways. - Lack of Exfoliation
Dead skin cells can accumulate and block hair follicles, making it harder for the hair to grow outward. - Waxing or Tweezing
These methods remove the entire hair from the follicle, and the new hair may have difficulty breaking through the skin surface. - Naturally Curly Hair
People with curly or coarse hair are more susceptible to ingrown hairs because the hair tends to curl back toward the skin. - Dry Skin
Dryness increases the likelihood of skin cell buildup, which can block hair follicles.
Symptoms and Identification
Ingrown hairs often manifest as small, round bumps on the skin, which may be:
- Red or dark in color
- Itchy or tender to touch
- Filled with pus (if infected)
- Accompanied by a visible hair loop under the skin surface
In some cases, particularly in individuals who regularly shave, the condition can progress to a more chronic form known as pseudofolliculitis barbae — a type of skin irritation resembling acne.
Areas Most Commonly Affected
- Face and neck: Particularly in men who shave regularly.
- Armpits: Frequent shaving and moisture retention make this area prone to ingrowns.
- Legs: Common in women due to regular shaving or waxing.
- Bikini line: One of the most sensitive and commonly affected regions.
- Chest and back: Can be affected in both men and women who remove body hair.
Potential Complications
While most ingrown hairs resolve on their own, complications can arise, including:
- Scarring: Especially if the bump is picked at or repeatedly irritated.
- Hyperpigmentation: Darkening of the skin in the affected area.
- Cyst formation: Deep ingrown hairs can form cysts that are painful and may require medical intervention.
- Infection: Bacterial infections can develop, leading to pus, increased pain, and spreading inflammation.
Prevention of Ingrown Hair
Prevention is key, especially for those prone to frequent outbreaks. Here are several methods:
Proper Shaving Habits
- Always shave in the direction of hair growth.
- Use a single-blade razor or an electric shaver.
- Avoid pulling the skin tight while shaving.
- Rinse the blade after each stroke.
- Use a clean, sharp razor — dull blades increase irritation.
Exfoliate Regularly
Use gentle scrubs, exfoliating gloves, or chemical exfoliants like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) to remove dead skin cells and keep hair follicles open.
Moisturize the Skin
Applying a non-comedogenic moisturizer keeps the skin soft and reduces the risk of hair getting trapped under the skin.
Avoid Tight Clothing
Loose-fitting garments allow the skin to breathe and reduce friction.
Consider Alternative Hair Removal Methods
Laser hair removal and electrolysis can provide more permanent results and significantly reduce the risk of ingrown hairs.
Treatment Options
If you already have an ingrown hair, several treatment methods can help:
At-Home Remedies
- Warm compress: Apply to soften the skin and encourage the hair to break through.
- Gentle exfoliation: Use a mild scrub or brush to remove dead skin and potentially free the hair.
- Topical solutions: Products with salicylic acid, glycolic acid, or tea tree oil can reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Do not pick or squeeze: This can cause scarring or infection.
Medical Treatment
If the ingrown hair becomes severely inflamed or infected, consider seeing a dermatologist. Possible treatments include:
- Topical steroids: To reduce inflammation.
- Antibiotic creams or pills: In case of bacterial infection.
- Manual extraction: By a medical professional using sterile instruments.
- Laser hair removal: A longer-term solution to prevent recurrence.
Home Remedies with Natural Ingredients
Some people prefer natural solutions to soothe the skin and accelerate healing. Here are a few popular options:
- Aloe vera: Known for its soothing and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Witch hazel: Acts as a natural astringent to reduce swelling.
- Honey: Antibacterial and hydrating.
- Apple cider vinegar: Has antimicrobial effects and can help exfoliate.
Use these remedies cautiously and discontinue if irritation increases.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a dermatologist if:
- The ingrown hair is persistently painful or inflamed.
- There are signs of infection (pus, excessive redness, spreading swelling).
- You frequently experience outbreaks.
- Home remedies do not provide relief.
- You notice cysts or scarring.
Early intervention can prevent long-term skin issues and more severe complications.
Cultural and Linguistic Note: «Ingrown Hair» in English
If you’re learning English or working in a bilingual setting, it’s useful to remember the correct term: ingrown hair. This phrase is widely used in dermatology, cosmetics, and skincare contexts. Related expressions include:
- «Shaving bumps» (a colloquial term)
- «Razor burn» (related but not identical — more about skin irritation than embedded hairs)
- «Folliculitis» (general inflammation of the hair follicle, which may or may not be due to ingrown hairs)
Examples of usage in English:
- «I always get ingrown hairs after waxing my legs.»
- «This exfoliating scrub helps prevent ingrown hairs.»
Understanding this term is particularly useful when buying cosmetic products abroad, speaking with professionals, or reading English-language guides and labels.
Conclusion
Ingrown hairs (ingrown hair) are a common and often preventable issue. While they may seem minor, recurring or infected ingrown hairs can lead to discomfort and skin complications. With proper hygiene, improved shaving techniques, and a consistent skincare routine, it’s possible to reduce the frequency of these unwanted bumps. For chronic cases, medical or cosmetic interventions like laser treatments offer a more permanent solution.
Whether you’re looking to expand your English vocabulary or simply want healthier, clearer skin — understanding how to manage and prevent ingrown hairs is an essential aspect of modern beauty and wellness routines.
 Здоровье и питание
Здоровье и питание